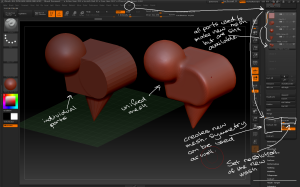
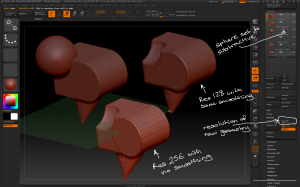
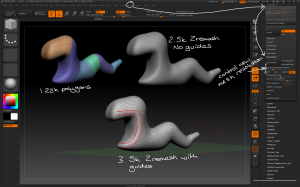
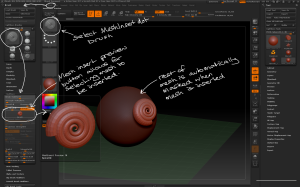
Introduction to Zbrush Digital Tutors
Pixols and the 2.5D canvas
– a pixol is a pixel that contains colour, depth, and material information.
– open the tool quick menu to select 2.5D brushes. 2.5D brushes can have strokes and alphas applied to them like sculpting brushes.

open the tool quick menu to see the 2.5D brushes.
– pixols can be tranformed using the Move, Scale and Rotate buttons. Select Draw to continue drawing in 2.5D.

Pixols drawn on the canvas can be transformed using the move, scale and rotate tools
– use EraserBrush to remove pixols from the canvas.

Use the EraserBrush to remove pixols from the canvas.
– materials and colours can be changed during the drawing to overwrite pixols already on the canvas.

the material and colour applied to the pixols can be changed during the drawing.
– disable Zadd / Zsub during the drawing to avoid adding depth to pixols already on the canvas, only painting with colour and / or material.
– Mrgb allows for changing colour and material of pixols on the canvas without affecting depth.
–RGB allows for changing colour of pixols on the canvas without affecting depth or material.
– Mrgb / RGB buttons can be disabled entirely to allow drawing depth without affecting the colour or material of the pixols.

Use combinations of ZAdd/Zsub, Mrgb and RGB options to draw with different depth, colour and material affects.
– Document > Save As saves the canvas out as an image, not a 3D model.
– SnakeHookBrush allows for dragging out tendrils with depth.
– FibreBrush allows for covering pixols in fibres / hair

Other brushes can be combined to get interesting 2.5D effects
– SphereBrush always paints with a perfectly round edge, which can be made larger with more pen pressure or larger strokes.

The SphereBrush with different strokes.
– AlphaBrush draws in the shape of the current Alpha at a single depth until a new stroke is started.
– Smudge brush can be used to smear pixols around on the canvas. Combining different strokes and alphas will give different effects.

Different effects using the Smudge Brush with different strokes and alphas.
– Hook Brush can be used to pull pixols out. LMB + Anti-clockwise spirals shrinks the pixols, while LMB + Clockwise spirals enlarges them. Hook Brush can be combined with alphas for different effects.

The effects of the Hook Brush using spiral gestures and alphas.