Introduction to Zbrush Digital Tutors
Working with Polygroups
– Polygons can be hidden at any time, holding Ctrl + Shift activates the SelectRect tool; dragging a rectangle then releasing hides everything that isn’t in the green box.

Ctrl + Shift enables the selection tool, which hides everything outside the selection box.
– Ctrl + Shift + LMB click outside the model reveals the hidden polygons – Ctrl + Shift + Drag outside the model inverts the visibility, revealing the hidden polygons and hiding the visible polygons. – Ctrl + Shift + Alt hides any polygons in the red box.

Ctrl + SHift + Alt hides any polygons inside the red box.
– models can be modified once polygons are hidden eg Tool > Geometry > Delete Hidden will delete any hidden polygons, making an open mesh.

– Polygroups are a quick and easy way to handle visibility by hiding entire parts of a model with a single click. – There are several tools to create a polygroup which can be found under Tool > Polygroups: the easiest way is by selecting some polygons then pressing Ctrl + W which assigns any visible polygons to a new polygroup.

– other options for creating polygroups include From Masking which converts any masked polygons into a new polygroup and Group Front which merges any polygons facing the camera.

POlygroups can be made based on visibility, colour or masking using these tools.
– Ctrl + Shift + LMB on a polygroup hides every other polygroup. Ctrl + Shift + LMB on the visible polygroup again to hide that group and reveal the hidden groups.
– Polygroups created at a low subdivision level are retained at higher subdivision levels.
– Polygroups can be made by masking areas then pressing Ctrl + W. This works the same as Tool > Polygroups > Group Masked.
– Use the PolishGroups slider next to Tool > Polygroups > Group Masked to create smooth-edged polygroups at higher subdivision levels. This modifies the geometry around the polygroup.

The polishgroups slider can be used to create smooth-edged polygroups from masked areas at the expense of deforming geometry.
– Slice tools can be used to quickly create polygroups: Ctrl + Shift brings up the Slice tool menu.

Slice tools can be used to quickly create lots of polygroups on a model.
– Holding Ctrl with the transpose tool selected eg Move or Rotate then clicking on a polygroup aligns the transpose tool with the normal of that polygroup while masking all other groups. Holding Shift while dragging the transpose line moves just that polygroup along the transpose axis.

An example of using polygroups and the transpose tool to manipulate a mesh.
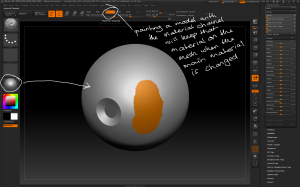
– POlygroups can be used to easily break a mesh into subtools by hiding a polygroup then using the Tool > Subtools > Split > Split Hidden command. The hidden polygroup is separated into a separate piece of geometry.

POlygroups can be used to create subtools by selectively hiding polygroups.
– POlygroups can be used to maintain crisp edges when subdividing using the Tool > Geometry > Edgeloop > Edgeloop command: Hide all but the desired polygroup, select the crisp button then press edgeloop. A new ring of polygons is added around the polygroup close to the border. Now when the model is subdivided this edge will stay sharper.

POlygroups and the edgeloop tool can be used to create features that stay crisp-edged even when the model is heavily subdivided.